Reddit post cracks us up
Funny (and informative) post from David Curiel, the concierge at the Whisper Valley community.
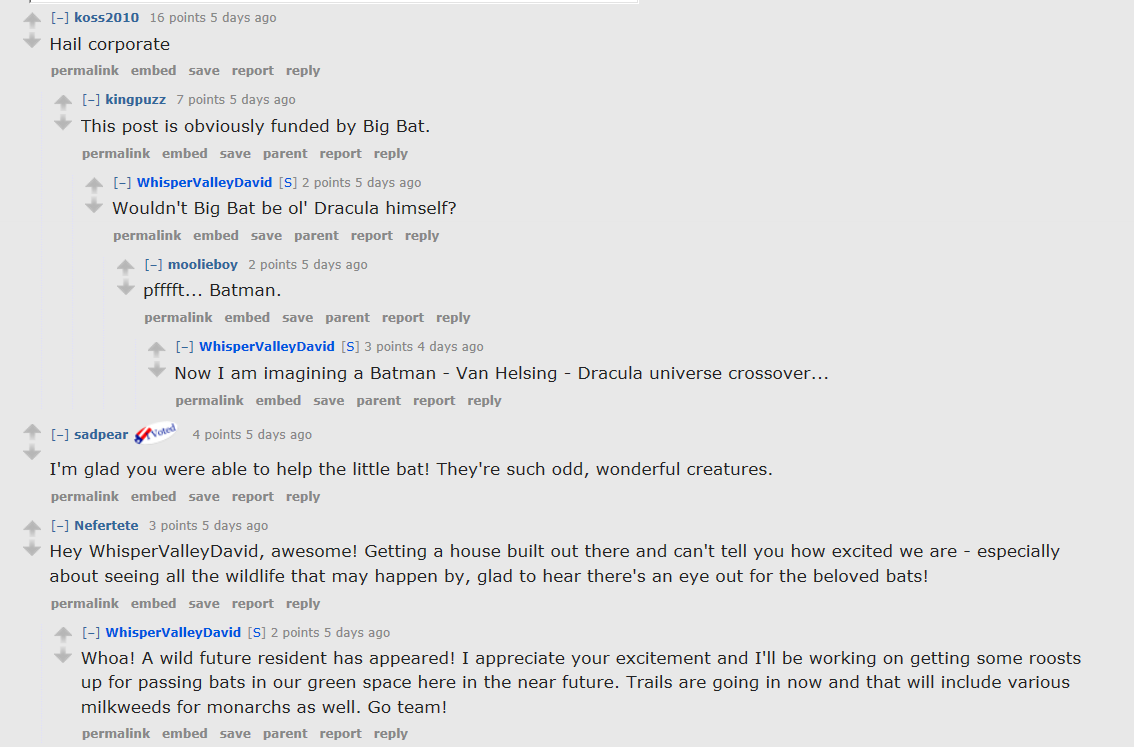
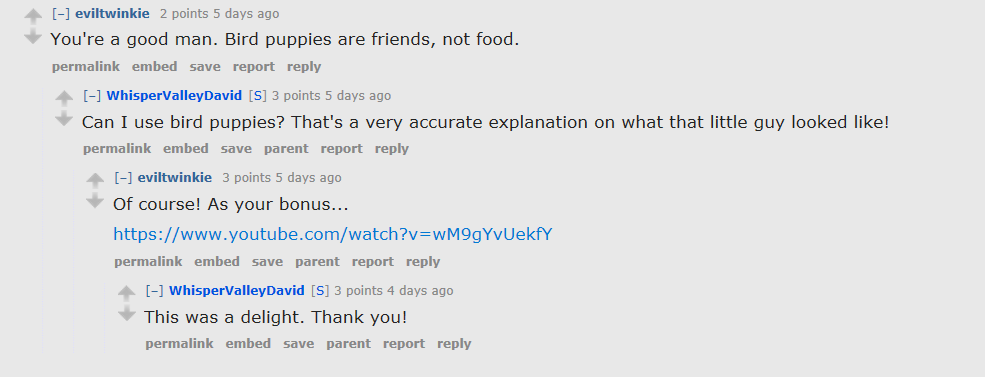
Funny (and informative) post from David Curiel, the concierge at the Whisper Valley community.


We’re not usually ones to toot our own horns, but these notes in our Bat Journal on our Information Table at Congress Avenue Bridge meant a lot to us.
Laura is great friends with Adria Lopez Baucells, whom we greatly admire, and Jordi knows Carles Flaquer, who visited our facility a few years back and is a wonderful person and dear friend.

Congress bats climbed to altitude directly over the bridge Saturday night, then turned & headed way South, with the wind. Great visit with Laura & Jordi from Barcelona! These lovely and gracious scientists are friends of our favorite bat people Adrià López Baucells & Carles Flaquer from Museu de Ciències Naturals de Granollers. This group is doing great work and we just love them. Look them up, follow them, and be awed!
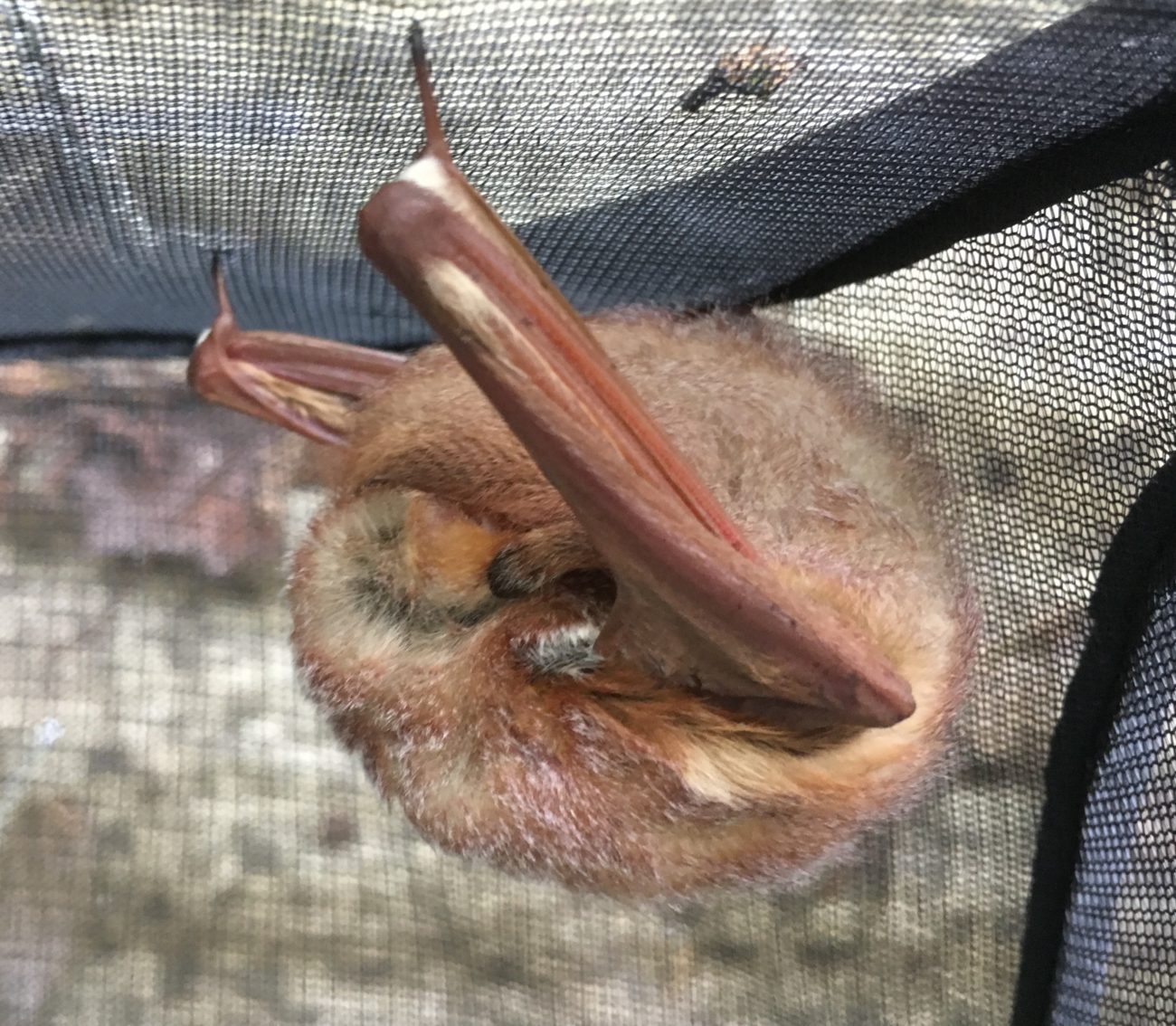
This red bat is using her thumbs to stabilize her snooze on this windy day. She has her butt blanket pulled right up over her eyes and it looks like she’s closing her ear with her foot! She was found emaciated on the UT campus but is eating well and will be good to go in a few days. #batifyatx #batifyaustin #austinbats #atxbats #easternredbat #aesomebats

We got lucky on Friday the 13th and had lovely weather for our education table at the Bat Viewing Area.
We shared the wonders of bats with scores of out-of-towners.
We so enjoyed meeting Sonia from Austria, Anne from France, Ali & Xav from Paris, and that group of impressive women in town for the Anthropology conference, from Virginia, Canada, the UK and Cyprus.
What fun! Thanks for visiting with us y’all!
We hope the bats were as lucky as we were! We at the Bat Viewing Area all watched on live radar as a lovely Seabreeze pushed insects toward the Hill Country and the Bracken bats foraged along the front. But then things changed.
The lovely Seabreeze turned into wicked storms from the northwest. Davis Blowout, Huber Limestone Mine, McNeil Bridge, and Congress Bridge bats all appeared to have been caught out in the storms. We hope they sheltered at McNeil to escape the worst of it.
Bats caught in hailstorms frequently experience broken wing bones from the hail. Guess we’ll see how many bats are found by humans and brought to us today. Bless their brave little hearts!
On the evening of April 8th radar picked up the largest flight we have ever seen from Frio Bat Cave. Our guess is there were as many as 17 million bats in the air at one time around 2:06 Universal Coordinated Time or about 8:57 Central Daylight Time.
They emerged around 7:19 pm CDT and some went 80 miles SE to around Christine, TX
Most went at least as far as 50 miles to crop fields around Pearsall, TX.
Old Tunnel & Bracken bats comingling.
So here it is.
Pd (Pseudogymnoascus destructans) has been detected in two sites in Kendal county and two sites in Blanco county. In addtition, it has been detected for the first time on a Mexican free-tailed bat.
We’re obviously devastated by the news that the fungus that causes WNS has arrived in our area. We, like everyone else here, had hoped for a little more time, but we knew it was coming. Although this is just the fungus, not yet the disease, we are nonetheless tweaking our rehabilitation protocols and stand ready to collaborate with state and federal agencies, BCI and other NGOs, and other Texas bat rehabilitators in monitoring and providing supportive care for Texas bats.
The following is an article by Zeke MacCormack, a San Antonio Express-News staff writer:
Published in the San Antonio Express-News April 5, 2018
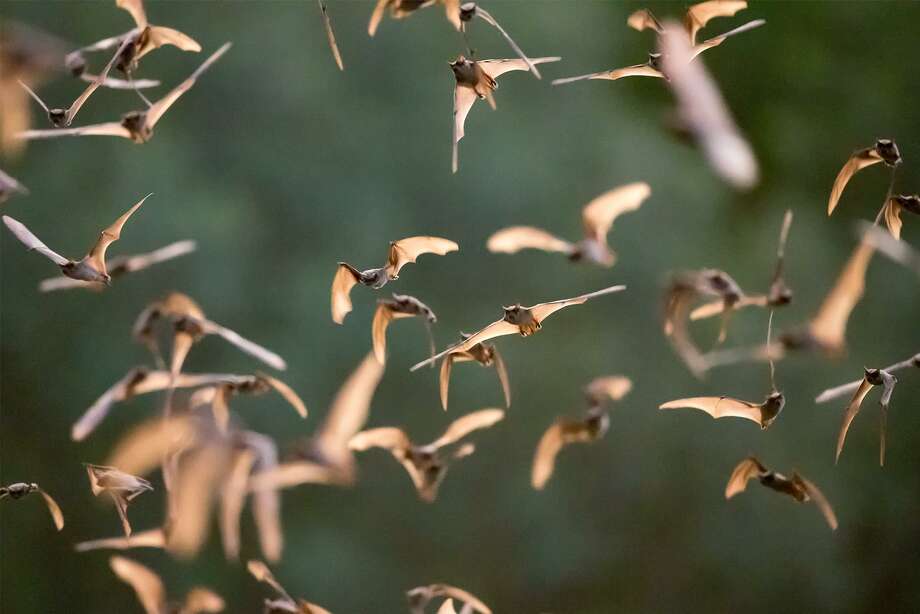

Photo: Marvin Pfeiffer, Staff / San Antonio Express-News
Mexican free-tailed bats emerge from the Bracken Cave at dusk to foray for food on Tuesday, Sept. 19, 2017.
In a double dose of troubling news, the fungus blamed for killing millions of East Coast bats since its discovery there in 2007 has been found in Central Texas and on a Mexican free-tailed bat — both firsts.
However, the Texas Department of Parks and Wildlife announcement of those discoveries Wednesday noted that no Texas bats have been found exhibiting signs of the malady known as “white nose syndrome.”
“Biologists say it usually takes a few years after detecting the fungus for the disease to manifest,” said the release that identified four new Texas counties where Pseudogymnoascus destructans fungus had been found, bringing the total to 10.
It previously was found on cave bats, tri-colored bats and Townsend’s big-eared bats.
In the San Antonio region, the fungus was detected on bats at two sites in Kendall County and two sites in Blanco County.
Kendall County is now the southernmost location in the nation where researchers have discovered the fungus, which was first detected in Texas in 2017 in the Panhandle, officials said.
The deadly illness typically strikes hibernating bats, causing declines of winter populations by more than 90 percent in some locations.
So its presence in free-tailed bats, which migrate rather than hibernate, raises a new series of concerns.
“They migrate in huge populations all over the country so they could spread the disease much faster,” said Jonah Evans, a TPWD mammalogist
The Mexican free-tail bat carrying the fungus was found at the Old Tunnel State Park in Kendall County, he said.
Evans described researchers as shocked by the results of testing on skin swabs that were collected from bat wings and muzzles between December and last month by a coalition of biologists from Bat Conservation International, Texas A&M University’s Department of Wildlife and Fisheries Sciences and its Natural Resources Institute.
“We were disappointed to see that it had moved southward as fast as it has,” Evans said. “We all expected it would move around the state, but it’s kind of shocking to see it happen this fast.”
The recent testing also found the fungus on bats in Foard and Wheeler counties, in North Texas, officials said.
The TPWD release said, “Because bats usually produce just one offspring per year, researchers are concerned it could take many decades for some populations to recover from a major decline.”
A widespread outbreak of the deadly disease in free-tailed bats could hold financial implications for agricultural producers who rely on the winged mammals to eradicate insects that feed on their crops.
The estimated value of bat pest control is $1.4 billion annually in Texas, the TPWD release says.
“Mexican free-tailed bats are key predators of agricultural pests in Texas, primarily moths that feed on corn and cotton,” said Mylea Bayless of Bat Conservation International.
“Since white nose syndrome is a disease of hibernating bats, we’re cautiously optimistic that Mexican free-tailed bats — which don’t hibernate — will fare better than other species in terms of contracting the disease and experiencing mortality from it,” she said.
The free-tailed bat also is an iconic presence, she said, drawing visitors watch them emerge by the millions from Bracken Cave just north of San Antonio, the Congress Avenue Bridge in Austin and other major colonies.
“This bat is special to Texas, which is one of the reasons that this news is particularly distressing,” Bayless said Wednesday.
Beyond trying to track the spread of the fungus, she said, “Bat conservation International is working with the Texas Parks and Wildlife Department and others to explore and test potential treatments for white nose syndrome.”
Zeke MacCormack is a San Antonio Express-News staff writer. Read more of his stories here. | zeke@express-news.net | @zekemac